Search Domains
- Updated on Apr 17, 2024
- 5 minutes to read
- Search Domains Overview
- Pre-requisites
- Steps to Configure a Search Domain
- Prioritizing Search Domains
Search Domains Overview
Windows File Sharing is a standard way to make files stored on one device accessible on another device over a network. It is designed to work in a local area network (LAN) environment; when users are remote, virtual private networks (VPN) are typically used to connect a file share.
To simplify file sharing, admins often leverage search domains. Search domains allow end users to use a shorthand reference (i.e., a hostname) to navigate to a fully-qualified domain name (FQDN). These short-hand references are easier to recall, and so they simplify the file sharing process. End users can enter a short-hand search string (e.g., /new-host) and Search Domains will append the domain name and the top-level domain (e.g., corp.internal), making up a fully-qualified domain name (e.g., new-host.corp.internal) that can be resolved to an IP address, thus completing the file share.
Banyan’s Search Domains feature is available within our VPN Service Tunnel’s configuration. This doc lays out the steps required for admins to configure Search Domains in a Service Tunnel in their org.
Pre-requisites
- A registered Service Tunnel
Steps to Configure a Search Domain
1. In the Command Center, navigate from Private Access > Service Tunnels, and select + Add Service Tunnel or select an existing Service Tunnel to configure Search Domains within.
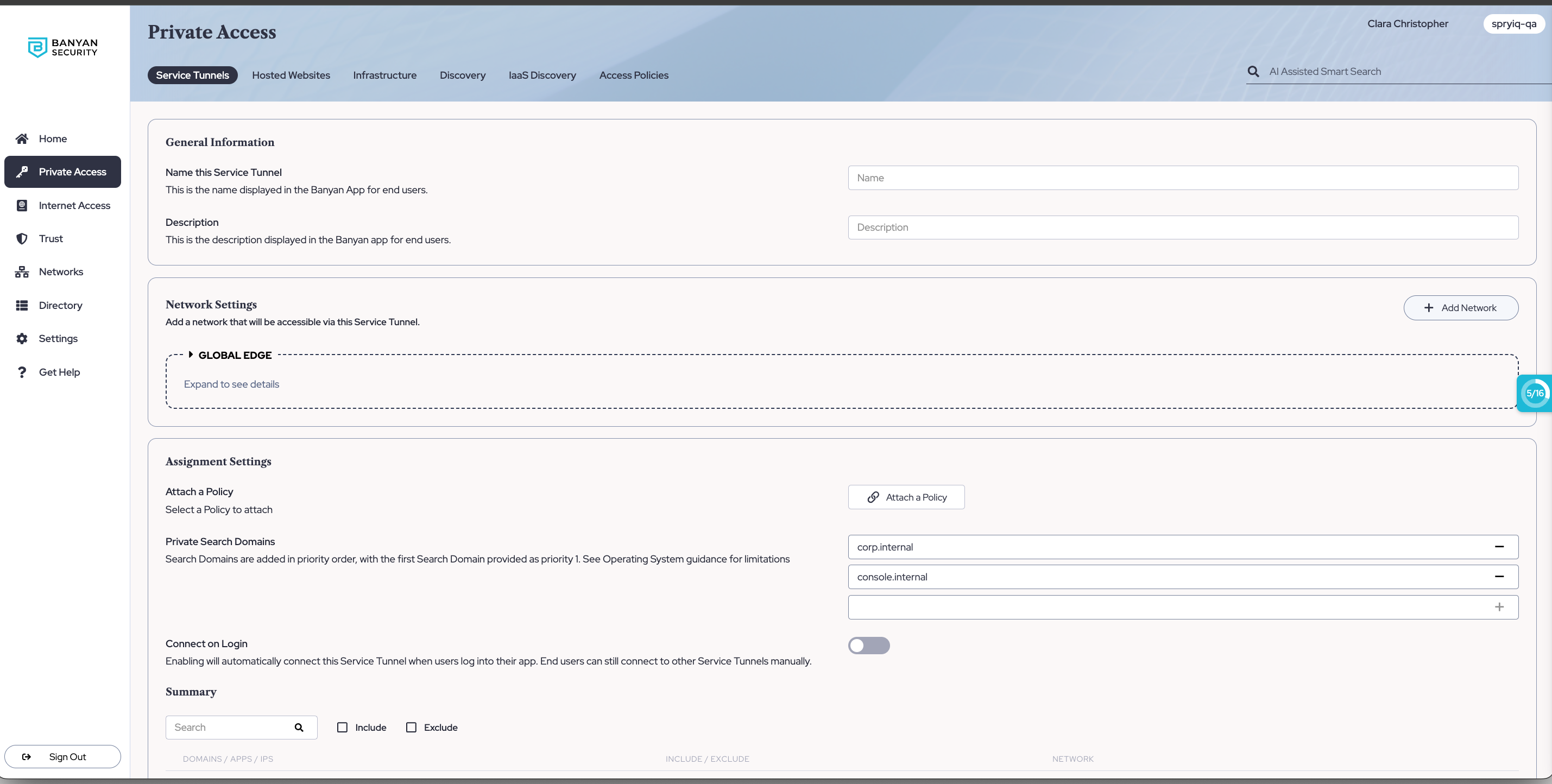
2. Under Assignment Settings (at the bottom of the configuration form), in the Private Search Domains field, enter a search domain to navigate end users to.
3. Optional: Add additional search domains to navigate end users to.
Note: Search domains entered are in order of priority; the first search domain entered is the highest priority and will take precedence over the second search domain. Ensure that search domains are entered in the correct priority order for your purposes.
Prioritizing Search Domains
Often, a single hostname (e.g., /new-host) can apply to multiple search domains (e.g., new-host.corp.internal AND new-host.console.internal). Admins must configure the order of priority of configured search domains.
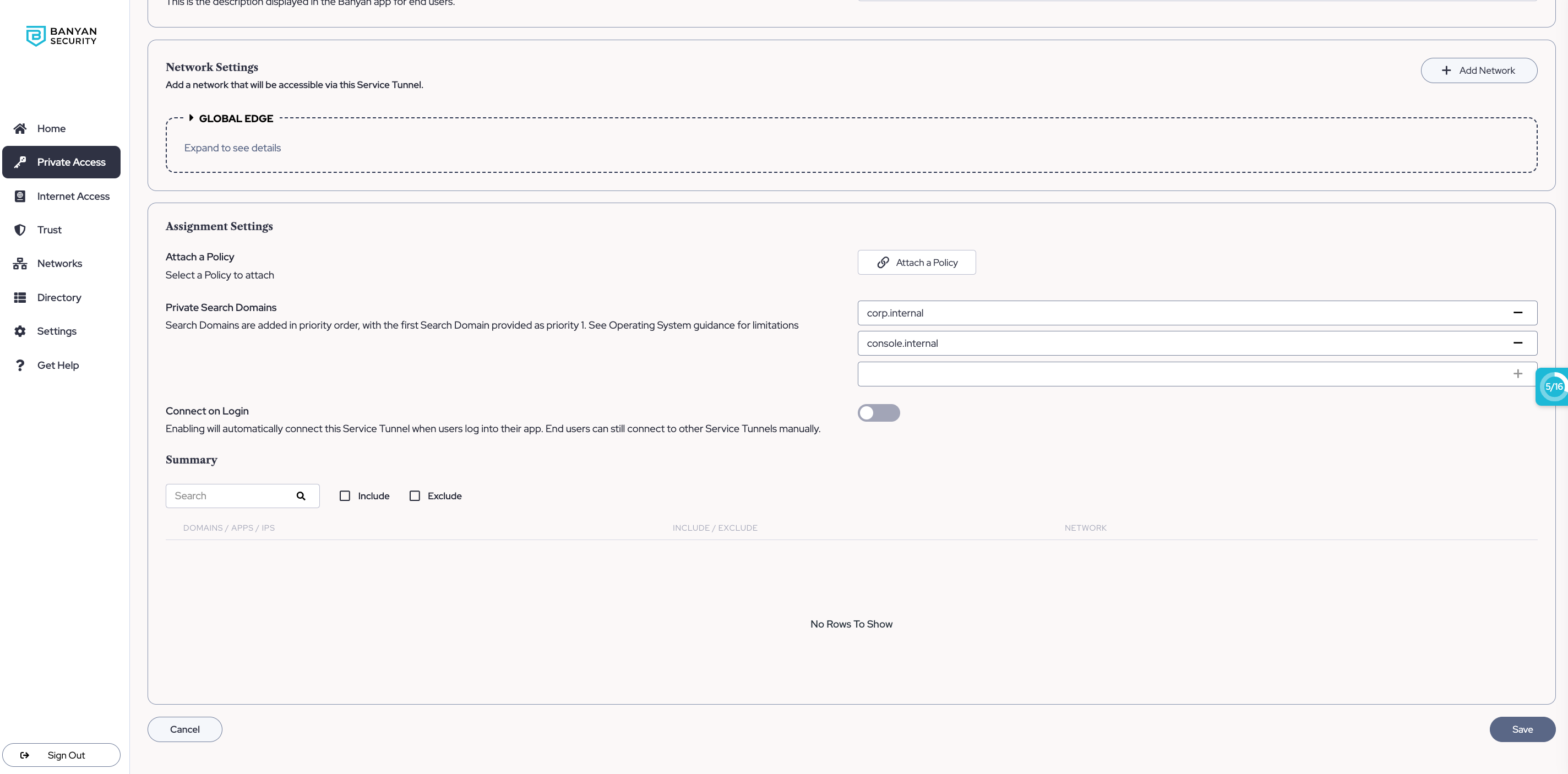
In the example above, the short-hand new-host would attempt to resolve to new-host.corp.internal first; if this doesn’t exist, it will then attempt to resolve to new-host.console.internal.
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
We’re happy to help. Contact our team.